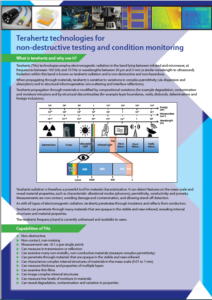
Introducing Terahertz
When we refer to terahertz, we are referring to photons radiated within the terahertz (THz) region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
THz, is a unit of frequency, defined as one trillion (1012) cycles per second or 1012 hertz. The THz region lies between the microwave and infra-red regions and subsequently shares some properties with each of these. The THz region is commonly considered to encompass the frequency range of 0.1 to 3 THz.
THz photons are naturally emitted from objects with a temperature greater than 2 degrees Kelvin. SubTera’s technology is passive, which means it functions by receiving THz photons emitted from other structures.
Capabilties of Terahertz Inspection
THz photons transmit through many materials, however they are attenuated heavily by liquids and metals. Liquids absorb THz photons and metals reflect them, therefore SubTera’s THz technology cannot inspect inside metals and liquids.
THz photons that transmit through materials can be used for material characterisation and internal or underlying feature inspection.
THz photons are non-ionising, therefore they do not present the same health and safety risks as X-ray inspection. They can however be used as an alternative to X-rays for producing suitably high resolution images of internal features within an object.
Applications
There are many applications for THz inspections within the high-value manufacturing, processing and quality control industries. Due to the properties of many non-metallic materials, THz inspections can be used to see internal or concealed defects, and to detect the presence of foreign objects within a material.